Introduction: Isatuximab, a CD38 monoclonal antibody (mAb), targets a specific CD38 epitope to induce myeloma cell death. Based on the results of the Phase 3 ICARIA-MM study, isatuximab (Isa) plus pomalidomide (P) and dexamethasone (d; Isa-Pd) is approved in adult patients (pts) with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM) who have received ≥2 prior therapies. Prior to Isa-Pd regulatory approval, Isa was available in France under early access programs (EAPs). IMAGE is a non-interventional, retrospective cohort study of pts treated with Isa-Pd under the French EAPs. In the IMAGE overall effectiveness population (median follow-up 14.2 months [mo]), median progression-free survival (mPFS) was 12.4 mo; overall response rate (ORR) was 46.3%; 27.9% of pts achieved a very good partial response (VGPR) and best response was VGPR for 60.3% of pts. In the current myeloma landscape, not all pts with RRMM have received a prior anti-CD38 mAb, particularly where access is difficult; thus, the real-world effectiveness of Isa in daratumumab (dara)-naïve pts needs to be assessed in light of the Phase 3 APOLLO and ICARIA-MM trials investigating dara-Pd and Isa-Pd in dara-naïve populations. Effectiveness results from the IMAGE subgroup analysis of dara-exposed and -refractory pts have been presented previously. Here, we describe results for dara-naïve pts based on prior lines of therapy (LOT) and lenalidomide (len)-refractory status.
Methods: Data were collected from medical records of adult pts with RRMM who received ≥1 dose of Isa under the EAPs from 29 Jul 2019-1 Sep 2020. The effectiveness analysis was restricted to pts with ≥1 year of follow-up after Isa initiation. PFS was defined as the time from Isa-Pd initiation to date of disease progression or death. VGPR was defined as a ≥90% reduction in serum or urine M-protein, or in the difference between involved and non-involved free light chain. The description of adverse events (AEs; verbatim) was recorded as a reason for treatment temporary or permanent discontinuation or dose reduction. Data were recorded per the subject's medical file. No specific grading was performed.
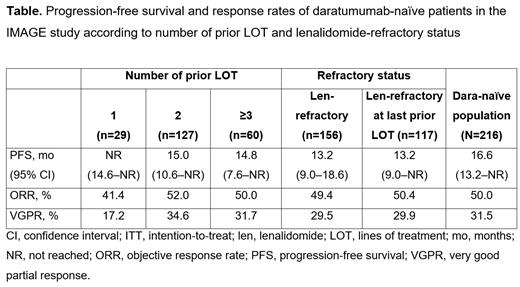
Results: The safety population included 299 pts who received ≥1 Isa dose under the EAPs; of these, 294 received ≥1 Isa dose and met all inclusion/exclusion criteria, thus comprising the effectiveness population. Within the overall effectiveness population, 216 (73.5%) pts were dara-naïve; among them, 13.4%, 58.8%, and 27.8% received 1, 2, and ≥3 prior LOT, respectively; 72.2% were len-refractory (median 2 prior LOT); and 54.2% were len-refractory at last prior LOT. At a median follow-up of 14.2 mo, mPFS (95% CI) in dara-naïve pts was not reached (NR; 14.6-NR), 15.0 mo (10.6-NR), and 14.8 mo (7.6-NR) with 1, 2, and ≥3 prior LOT, respectively; 13.2 mo (9.0-18.6) in those refractory to len; and 13.2 (9.0-NR) in those refractory to len at last prior LOT. ORR (of which, VGPR) was 41.4% (17.2%), 52.0% (34.6%), and 50.0% (31.7%) in pts with 1, 2, and ≥3 prior LOT, respectively; 49.4% (29.5%) in len-refractory pts; and 50.4% (29.9%) in len-refractory at last prior LOT pts (Table). At least 1 AE was reported in 53 (24.4%) pts in the dara-naïve safety population (n=217): 7 (24.1%), 32 (25.2%), and 14 (23.0%) in the 1, 2, and ≥3 prior LOT subgroups, respectively; 41 (26.1%) in the len-refractory subgroup; and 32 (27.4%) in the len-refractory at last prior LOT subgroup. AEs led to permanent Isa discontinuation in 3 (2.4%) pts with 2 prior LOT; 3 (1.9%) len-refractory pts; and 2 (1.7%) len-refractory at last prior LOT pts. The most common AEs were blood and lymphatic system disorders, occurring in 39 (18.0%) pts. Infections and infestations were reported in 2 (0.9%) pts: 1 had received 1 prior LOT and 1 had 2 prior LOT; both pts were len-refractory at last prior LOT.
Conclusions: In the dara-naïve populations from APOLLO (dara-Pd) and ICARIA-MM (Isa-Pd), mPFS was 12.4 and 11.1 mo, respectively. This subgroup analysis of IMAGE provides real-world evidence of Isa effectiveness in dara-naïve subgroups: Isa-Pd demonstrated a high mPFS of 16.6 mo in dara-naïve pts and meaningful mPFS at first and subsequent relapse, including in difficult-to-treat len-refractory pts; mPFS was generally comparable to that of the overall effectiveness population. No new safety signals were observed compared with ICARIA-MM. However, the incidence of some AEs like infections was low, possibly due to the retrospective nature of the study.
Funding: Sanofi.
Disclosures
Leleu:Novartis: Honoraria; Merck: Honoraria; Takeda: Honoraria; BMS/Celgene: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria; Sanofi: Honoraria; GSK: Honoraria; Harpoon Therapeutics: Honoraria; AbbVie: Honoraria. Perrot:Abbvie, Adaptive, Amgen, BMS, Janssen, Pfizer, Sanofi, Takeda: Honoraria. Karlin:AbbVie, Amgen, Celgene, Janssen, Sanofi, Takeda: Honoraria; Amgen, Celgene, GSK, Janssen, Takeda: Consultancy. Touzeau:Bristol Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Manier:BMS: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria; Abbvie, Amgen, Celgene/BMS, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche, Sanofi, Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Honoraria. Belhadj Merzoug:BMS: Research Funding; Amgen, BMS, Janssen, Sanofi: Honoraria; Amgen, Janssen, Pfizer, Sanofi, Takeda: Other: Travel Support. Zunic:Abbvie, Janssen, Sanofi: Other: Travel Support. Schiano De Colella:Pfizer, Amgen: Other: Accomodation; Janssen, Sanofi, GSK, Abbvie: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Tekle:Sanofi: Current Employment. Gaucher:Sanofi: Current Employment. Decaux:Janssen, BMS, GSK, Sanofi, Takeda, Roche, Gilead: Honoraria.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal